Treatment is an important, and many times vital, part of successfully alleviating this persistent obsessive-compulsive disorder. Accepting that you have OCD can be a difficult process, as can deciding how to approach this condition. But as our understanding of OCD increases, the benefits of advanced therapies, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), are gaining greater recognition from researchers and field professionals. TMS offers patients and their loved ones a new form of therapy. Read on to test your knowledge and learn more about this cutting edge treatment for OCD.
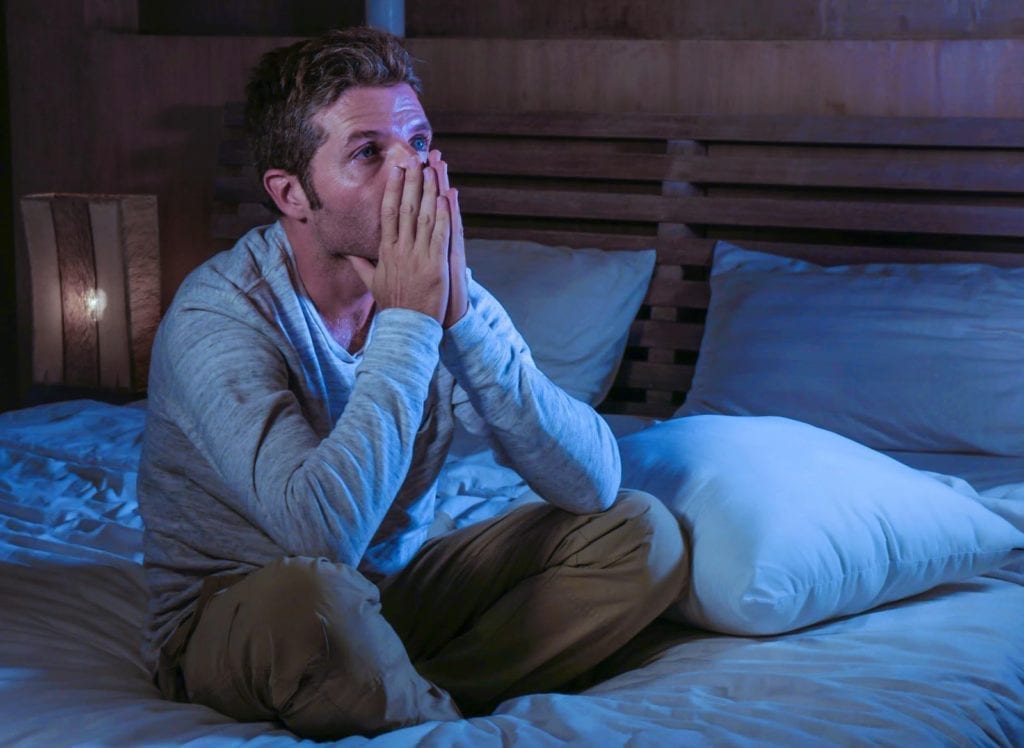

Obsessive-compulsive disorder is an anxiety-based condition recognized as its own mental health disorder. OCD is defined as obsessive thoughts that trouble the individual experiencing them and the compulsive actions they take in an effort to assuage the anxiety that occurs as a result of their constant worrying over these thoughts.
Obsessive thoughts usually manifest as being overly concerned with a specific aspect of daily life. The four most common OCD themes are:
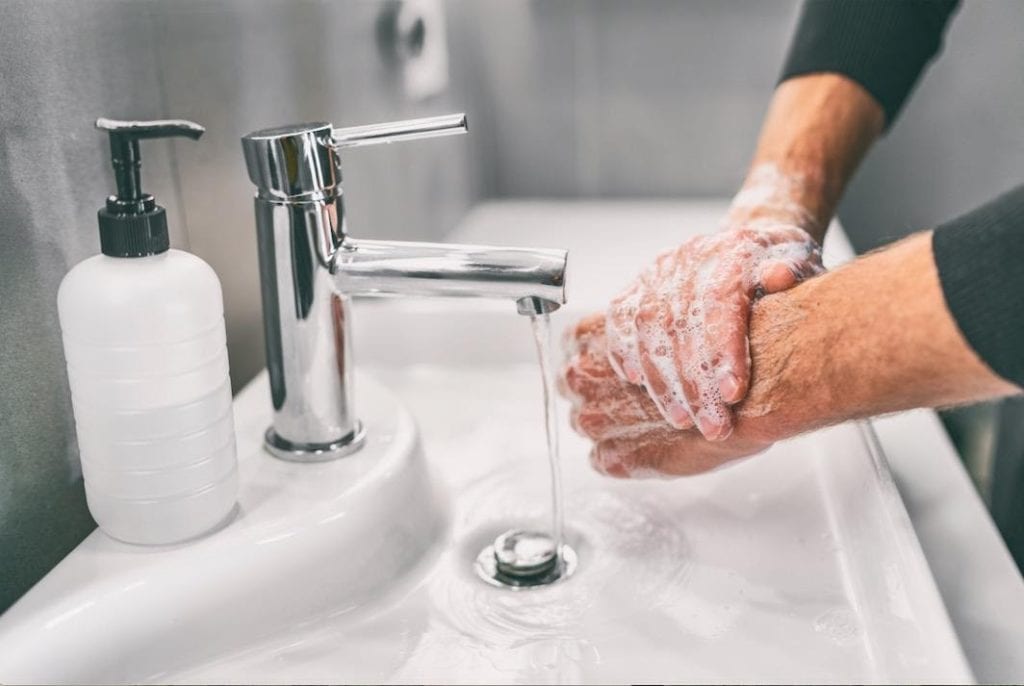

In addition to these and other intrusive and unwanted thoughts, many of those facing OCD also contend with compulsive actions. These actions can be extremely diverse and do not necessarily have to be thematically linked to the main area of concern that caused them. Cleanliness-based OCD, for example, can cause an individual to repeatedly wash their hands, only use their right hand to pump out their liquid soap, and switch out their body wash every four days. OCD-related behavior can be repetitive and ritualistic. While the original intent behind it was to decrease the level of stress brought about by the OCD-related thoughts and worries, eventually these actions add to the individual’s anxiety once they realize they can no longer avoid carrying them out. As a result, the individual facing this condition feels less in control of their life as frustration, distress, and hopelessness begin to set in.
TMS, and particularly Deep TMS, have been shown to help alleviate OCD symptoms and provide patients with much needed relief. This treatment utilizes electromagnetic fields to safely and effectively regulate the neural activity of brain structures found to be linked to OCD.
While traditional TMS offers some beneficial reduction of OCD symptoms, Deep TMS has been shown to go a step further. The Deep TMS patented H-Coil technology is able to reach wider and deeper areas of the brain directly. This avoids targeting issues and successfully normalizes the neural activity of the relevant brain structures.
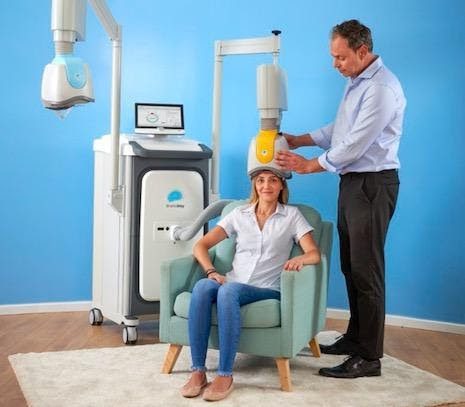
As a non-invasive treatment, Deep TMS does not cause any significant or long-lasting side effects, does not require the use of anesthesia, and can be incorporated into one’s daily schedule. Deep TMS can also be combined with other forms of treatment, such as antidepressants or CBT, thereby increasing their overall efficacy.
Deep TMS has also been shown to alleviate the OCD symptoms of treatment-resistant patients who did not find psychotherapy or medication to be effective in battling their condition. Its ability to offer relief has been documented through a number of studies, as well as patients’ personal testimonials.
Now that you have become familiar with the above-mentioned basic features of OCD, it is time to see how familiar you are with the lesser-known facts and trivia associated with this condition:
Answer: B. Obsessive-compulsive disorder is considered to affect 1.2% of the world population, making it a relatively common affliction.
Answer: C. OCD is commonly seen in both men and women at equal rates. That said, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM) refers to several gender-based differences. The main differences are that boys/men tend to develop OCD earlier than girls/women, that men are more likely to develop tics as part of their OCD, and that women are more likely to develop cleanliness-themed OCD while men are more likely to develop symmetry or forbidden thoughts-themed OCD.
Answer: A. It was not until 1877 that German psychiatrist Carl Westphal presented a distinct definition for an anxiety-based disorder that centers on obsessive thoughts and compulsive actions. However, symptoms of OCD, such as excessive worrying over non-threatening stimuli, were reported as early as texts from Ancient Greece.
Answer: C. An often-quoted 2001 study by the World Health Organization (WHO) lists OCD among the top-ten most debilitating illnesses when it comes to loss of income and quality of life. However, research since then has found that OCD can be effectively treated through a number of well-established therapies, making this disorder more manageable. OCD is still very much considered a serious condition and the DSM-V stresses that its presence can significantly impair an individual’s occupational and social functioning. The DSM-V also states that roughly 25% of those battling this condition will attempt to take their own lives.
Answer: A. According to the DSM-V, OCD occurs at an equal percentage across the globe. Moreover, the four major OCD themes of cleanliness, taboo thoughts, “just right” thinking, and catastrophizing all occur at similar rates around the world.
Answer: B. Antidepressant medication of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors family is considered a first-line treatment for OCD. This is due to its ability to act as a mood elevator that can lower one’s anxiety by keeping the neurotransmitter serotonin active for a longer period of time. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that is also considered a first-line OCD treatment. CBT works by focusing on the patient’s experienced thoughts, feelings, physical sensations, and behaviors associated with their OCD. CBT can help reduce patient’s anxiety over the appearance of these symptoms while encouraging them to consider more beneficial responses to triggering, anxiety-causing stimuli. Due to their efficacy and safety, both SSRI antidepressants and CBT are usually the go-to treatments for patients battling OCD.
Answer: B. Roughly 30% of individuals with OCD find first-line treatments, mainly SSRIs, to be a relatively ineffective form of therapy. Many of them turn to available alternatives in the hopes of finding a solution.
Answer: A. SSRI medication has been approved by the FDA to treat OCD in addition to depression and other anxiety-based disorders. Deep TMS is an advanced form of TMS and the only non-invasive medical device to be FDA-cleared with supporting clinical data to treat OCD. Antioxidant therapy is considered a promising direction that still requires more research. Tricyclic medication is also not an FDA-recommended OCD treatment: the drugs in the tricyclic group of medications require a higher dosage to be effective in treating OCD, and as a result they can cause more severe side effects.
0-2 Correct Answers: Seems like you could benefit from some more info on OCD! Check out BrainsWay’s OCD Section in the Knowledge Center for lots more interesting articles!
3-5 Correct Answers: You’ve definitely read about this condition and are interested to learn more! Check out BrainsWay’s Knowledge Center for original articles on a variety of mental health topics!
6-8 Correct Answers: Wow, we’ve got an expert here! You certainly know your OCD info! You might be interested in learning even more about this condition and a number of others by visiting BrainsWay’s Knowledge Center!